Major Research 2C Research on Effective Use of Existing Infrastructure Facilities
Background and Objectives
There is strong demand to improve the functions of existing infrastructure and use them effectively as possible. Requests include measures to handle increasing cargo volume and larger ships and vessels, diversification of airport functions, and countermeasures to deal with existing facilities which can no longer be used due to increased external forces and other reasons. In addition, regarding waste disposal sites at ports which accept industrial and non-industrial waste, there is social demand for the highly effective use of them. On the other hand, it has become difficult to secure disposal sites which accept soil dredged from water channels for shipping routes. Accordingly, it is necessary to prolong the life of soil disposal sites.
Therefore, we will develop the following: techniques to improve the functions of existing infrastructure and to renew and efficiently change the intended use of existing infrastructure; techniques to reduce or effectively utilize construction byproducts; and techniques to effectively utilize waste disposal sites at ports.
Research Topics
Research and development comprises the following three subthemes:
1.Research on techniques to improve or renew existing facilities
We have already conducted research and development on improving existing facilities including deepening existing quaywalls. However, such improvements were made using techniques for newly-built structures. Hereafter, we will investigate methods of evaluating ground characteristics, design methods, and geotechnical survey methods to improve and renew existing facilities. In such methods, the construction history, effects from neighboring structures, and other factors will be taken into account. We will also investigate ground evaluation methods and geotechnical information databases, both of which cover residual settlement and other phenomena, with the aim of long-term facility maintenance and management.
2.Research on effective use and techniques of treating construction byproducts
We will investigate the following techniques regarding dredged soil: improvement techniques to transform dredged soil into high-value added materials including composite soil, which provides habitats for benthic creatures, and solidified soil with high water permeability; and new volume reduction techniques. We will also investigate durability when solidified soil and slag composite soil are used in sea areas, the mechanical characteristics of composite ground materials containing various byproducts, crushable materials, and other contents, and methods of evaluating and managing the quality of these materials.
3.Research on management and utilization of waste disposal sites at sea
Regarding disposal sites at sea, technologies for seepage control works for site development have been progressed. However, research on post-construction utilization of such sites has not been conducted. Therefore, we will investigate the following which are necessary for utilization: foundations, construction methods, effects on impermeable layers, management methods of the internal water level at low cost, techniques to detoxify waste before land reclamation, and the medium to long-term strength and elution characteristics of solidified soil.
Activities in FY 2018
Based on measurements of unequal settlement of reclaimed land at airports, we continued to estimate settlement as we did in the previous fiscal year. As the undulating shape of the surface had not changed significantly from the previous year, and the coefficients of the estimated settlement curves almost converged, we judged that the prediction method using data accumulated over a set period of time and the curves that approximated those data was effective.
We used transparent soil to visualize the process of grout injection into different sandy grounds with varying fine particle fraction contents. Such grout injection experiments were conducted in a gravitational field and a centrifuge, where we evaluated the status of grout permeation around areas of the ground that had uneven contents, the effects on the ground in the surrounding area, under various conditions such as confining pressure, fine particle fraction content, and fine particle fraction distribution.
We examined the method of ground improvement to be applied to the ground between the piles at existing sheet-pile-type mooring wharves with coupled pile anchorage, which is intended to improve durability, by conducting 3-dimensional model experiments and numerical analyses. Then, we developed a numerical analysis method for application to actual cross sections, and used the method to design actual structures. In addition, we conducted 3-dimensional measurements on breakwaters built directly on soft ground, and confirmed that their point group data were useful for detecting any change in behavior, etc.
To be able to perform X-ray CT scanning of the ground on-site and understand various engineering characteristics from the acquired images, we developed equipment that enables X-ray CT scanning of a core sampled from the ground on-site, focusing on gravel grounds, and also conducted model-based verification experiments including various indoor CT scanning tests.
We used model cross sections and conducted numerical analyses to examine how increasing the height of a levee would alter its conditions, by using parameters such as the height of dredged soil, distance of a temporary bank from the bulkhead, structural and mechanical properties of temporary banks, and countermeasures for bulkhead bodies.
We also summarized the results of pile-installation and pile-removal experiments at a waste site that had been filled with incinerated ash. We started to investigate an insolubilization of contaminants by cement improvement technique and investigated deterioration promotion methods to study the deterioration of solidification-treated soil and eluviation of contaminant. As a result, regarding high-earlystrength cement, we achieved homogeneous deterioration of the specimens by compulsory permeation.
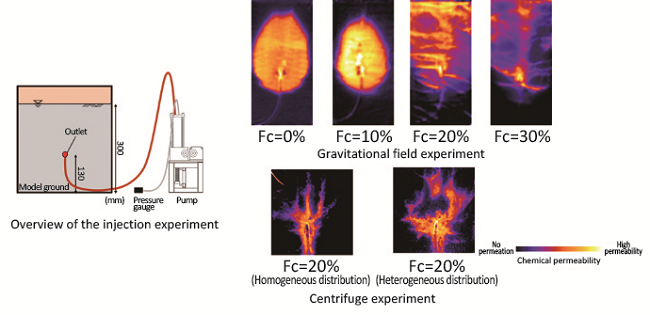
Example of a chemical injection process visualized during the model-based centrifuge experiment
(Potential effect of different ground conditions on the creation of improved areas)



