Effect of suppressing DEF expansion using surface coating
Major Research 2B Research on Life Cycle Management of Infrastructures
Background and Objectives
The ports, airports and coastal infrastructures that have been in service for a long time are increasing, but financial resources and the number of engineers for facility maintenance are limited. As important port, airport, and coastal infrastructure functions should be maintained, the strategic maintenance, renewal, and other measures to maintain such functions are strongly required.
Therefore, we are trying to establish methods for structure design and material selection which are excellent in terms of maintenance, and will develop techniques and technologies regarding various countermeasures for maintenance phase.
Research Topics
Research and development comprises the following three subthemes:
1.Research on technologies for prolonging the life of infrastructure
Regarding various construction materials in marine environments, we will conduct research on the following: evaluation of long-term durability, understanding of deterioration mechanisms, and investigation of the prevention effects of protective methods for steel structures. Especially, assuming that infrastructure is used overseas and on remote islands in Japan, we will investigate material characteristics for durability improvement under severe environments and under conditions in which low-quality material is used, and will investigate environmental-load reduction, durability improvement, and environmental harmonization. Regarding airport pavement, we will investigate methods for detecting the stripping of asphalt mixtures, measures to prevent such stripping, how the durability performance of airport pavement can be improved, and quick repair and rehabilitation techniques while construction quality, is still assured.
2.Research on systems for inspecting and diagnosing infrastructure
We will research and develop the following: inspection and diagnosing techniques using non-destructive and semi-destructive inspection methods and sensors, unmanned investigation devices including ROVs, non-contact thickness measurement system, and others. Especially, we will propose a health-monitoring system which utilizes sensors, as well as monitoring methods specialized for each member type.
3.Research on maintenance and management systems for infrastructure
We will conduct accelerated deterioration tests of members of port structures, investigate performance deterioration models which cover the entire lifecycle of structures, and validate such models through exposure tests in actual environments and through on-site investigation. We will also take into account the required properties and utilization of individual structures, budgets, and various limitations, and then suggest strategies of management of port-based and district-based groups of port structures.
Activities in FY 2018
We used long-term exposure facilities to study how to predict chloride-induced concrete deterioration, the electrolytic protection characteristics of steel bars in reinforced concrete, and the concentrated corrosion mechanism that affects steel materials. We also obtained data on the durability of various wood materials and reinforced concrete that utilized recycled frame materials.
We aimed to establish a method for predicting the deterioration of protective coating methods against corrosion. To achieve this goal, we conducted continuous experiments at Hazaki Observational Pier, including exposure tests on steel pipe piles to which anti-corrosion protective coating had been applied. We also conducted accelerated deterioration trials and exposure tests to further elucidate the deterioration mechanism of petrolatum coating methods.
We evaluated the durability of concrete, in which low-grade aggregate (coral aggregate) and seawater as mixing water had been used, and conducted exposure tests to develop a concrete-curing technique using seawater. We also evaluated the durability of highly corrosion-resistant reinforcing steel and surface coating materials through exposure testing.
We conducted a comparative evaluation of the aggregate gradation of airfield asphalt mixtures by indoor tests on their rutting resistance, moisture susceptibility, water permeability, and other characteristics, aiming to prolong the life of airfield asphalt pavement.
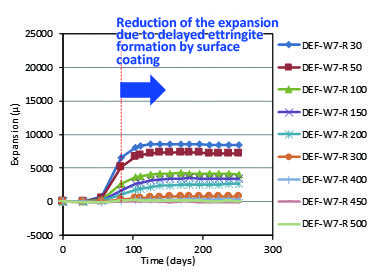
We studied the solidification of filling material in caisson-type outer walls as a preventive measure against local failure due to repeated collisions of wave-dissipating blocks, focusing on how such solidification work, strength of filling materials, and thickness of solidification would affect the load-bearing and impact-resistant capacities of those outer walls. In addition, we examined a method for monitoring the effects of repairs performed on prestressed concrete (PC) members that are prone to chloride-induced corrosion, in order to improve the repair techniques. We experimentally examined the feasibility of performing repairs by applying surface coating to protect expansion due to alkali-silica reaction and/or delayed ettringite formation, evaluated the effects of the method, and improved the existing model.
We organized points that must be considered while designing steel and concrete members for future maintenance purposes, and reflected some of them in revised technical standards. We also proposed a flow chart for determining use-conversion of existing caissons. In addition, we examined methods for inspecting and diagnosing PC hollow girders that utilize high-durability materials.
We conducted monitoring verification tests using an IoT-enabled inspection and diagnosis system and investigated optimal threshold values for the maintenance and management of sensors for checking the corrosion prevention effects of petrolatum lining method. We also examined what points should be monitored that would be useful for determining the usability of the superstructures of PC open-type wharves when major earthquakes occur. Also, the applicability of performing inspections using underwater drones was examined.
We introduced new operational support functions including a shooting-omission prevention function and an autonomous collisionavoidance function into the ROV for inspecting the superstructures of piers and then conducted on-site demonstration test.
To advance the process of formulating preventive and maintenance plans for port and harbor facilities, we performed case studies on model piled piers, while formulating renovation scenarios (selection of an optimal renovation method and timing) based on which those piled piers can be converted into a preventive maintenance, using LCC and NPV as evaluation indicators.