Major Research 2A Research on Enhancement of Port and Airport Performance for Industrial Competitiveness
Background and Objectives
Focused approaches on the following two matters are required:
- The population is decreasing, society is graying, and accumulated infrastructure is aging in Japan. In view of such problems, studies should be conducted on how to secure port and airport functions, which support the international competitiveness of Japanese industry and the vitality of the nation, and people's lives.
- With limited financial resources and workforce, studies should be conducted on how to efficiently and effectively implement maintenance, renewal, and repair works while efficiently using existing infrastructure and prolonging the life of overall facilities themselves.
Therefore, we decided to engage in research and development and other activities which are associated with improving the functions of ports and airports. In these activities, we are conducting comprehensive research and development throughout PARI on subthemes associated with international competitiveness including internationally strategic port policies and improvement of metropolitan airport functions (improvement of Haneda Airport).
The themes of this research address the development of specific technologies associated with international competitiveness including automated cargo works and construction information modeling (CIM). Regarding development of technologies which efficiently and effectively implement the following matters for port and airport facilities, the themes of other studies (1A, 2B, and 2C) address: improvement of largescale facilities, improvement of the quake resistance of facilities, maintenance and management after facility construction, and improvement of existing facilities.
Research Topics
1.Development and suggestion of efficient and suitable use which contains automated cargo systems through container terminal numerical simulations for multi berths
Focusing on internationally strategic container ports, we aimed to establish methods to effectively utilize Japan's narrow container terminals. With this goal, we will quantitatively evaluate the effects of off-dock loading/unloading as well as the effects of streamlining operations on reducing environmental burden and preventing congestion in front of gates. Then, we will use the evaluation results to establish strategies to effectively and comprehensively utilize container terminals.
2.Saving labor, shortening the work period, and reducing costs by using CIM
As part of construction information modeling (CIM) utilization, we will use construction-control data from a multi-beam sonar to establish a construction inspection method. With this method, we aim to save labor and achieve international standardization of construction-control inspection. By using CIM, we also aim to establish unmanned marine construction, in which Japan is lagging behind.
Activities in FY 2017
1.Development and suggestion of efficient and suitable use which contains automated cargo systems through container terminal numerical simulations for multi berths
We selected Minami Honmoku Pier MC1-4 of Yokohama Port for the study. In MC1-4, we quantified the number of waiting vehicle in front of gates and its effect on roads outside the terminal under different hypothetical gate conditions, configuration, handling capacities, and a reservation system through a numerical simulation using AutoMod.
After the simulation, we learned that, to avoid traffic jams within wharfs, operators should approach carefully including selecting a proper route for vehicles. Also, it was shown that the reservation system affects traffic-jam time dispersion and other phenomena.
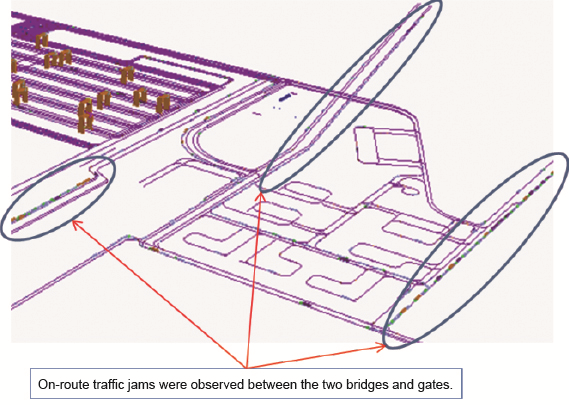
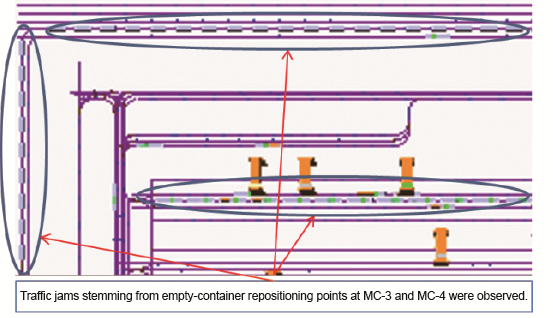
Observation of traffic-jam conditions under simulation. Carefully devised plans regarding route setting and repositioning points are required.
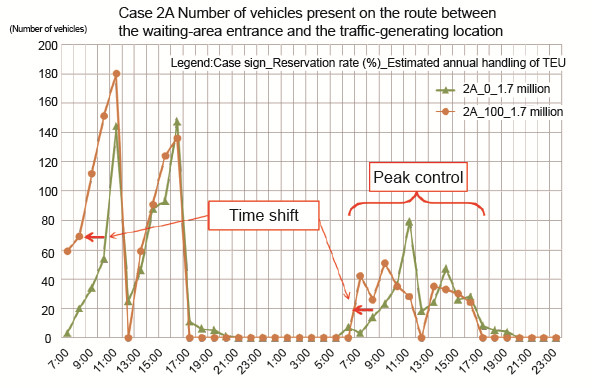
The example of simulation. Case 2A is a case in which vehicles are relatively concentrated at one gate. As compared to the green line (no reservation), the orange line (100% reservation) indicates that the 100% reservation system results in the earlier development of traffic jams than the no-reservation system; however, on days when vehicle numbers are relatively small (right), the 100% reservation system is controlled its traffic peaks. Regarding traffic-jam causes, the poor traffic capacity of routes in the wharf appears to have a significant effect.
2.Saving labor, shortening the work period, and reducing costs by using CIM
The Japan Coast Guard and international institutions, which regulate marine charts, addressed multi-beam sonar data; however, such operation even at works directly implemented by the government was included in the subjects of the turnover inspection standard from FY 2017. Therefore, government-led operational support was offered.



