Major Research Study on the volume reduction of dredged soil by electro-osmosis dehydration
According to increase size of vessels, a large amount of dredged material is occurred every year by dredging for the purpose of maintaining and improving navigation channels and anchorage areas, as well as for the purpose of increasing the depth in front of the wharf, etc. It is thought that the consolidation dehydration is effective volume reduction method of dredged soil.One of the measures to dispose of more dredged soil is to reduce the volume of dredged soil. One particularly promising approach is consolidation dehydration method by electro-osmosis. The electro-osmotic dehydration is the application of electric current to the soil through electrodes that are inserted into the saturated soil where water can be drawn from the anode to the cathode via electro-osmosis. By this process, dehydration of pore water occurs on the cathode side. For this research, the objective of the project is to examine the applicability of electro-osmotic dehydration as an effective method of reducing the volume of dredged sediments. As for our activities conducted in FY 2021, we built a consolidation test apparatus that could conduct electricity. We examined the electro-osmotic consolidation tests of Tokyo Bay clay and Kaolin to consider the effectiveness of electro-osmotic
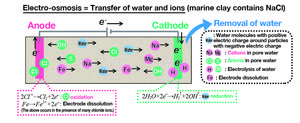
Illustration of electro-osmosis


Clay sample from Tokyo Bay, before and after the electro-osmotic consolidation and dehydration test



