Major Research 2C Research on Effective Use of Existing Infrastructure Facilities
Background and Objectives
There is strong demand to improve the functions of existing infrastructure and use them effectively as possible. Requests include measures to handle increasing cargo volume and larger ships and vessels, diversification of airport functions, and countermeasures to deal with existing facilities which can no longer be used due to increased external forces and other reasons. In addition, regarding waste disposal sites at ports which accept industrial and non-industrial waste, there is social demand for the highly effective use of them. On the other hand, it has become difficult to secure disposal sites which accept soil dredged from water channels for shipping routes. Accordingly, it is necessary to prolong the life of soil disposal sites.Therefore, we will develop the following: techniques to improve the functions of existing infrastructure and to renew and efficiently change the intended use of existing infrastructure; techniques to reduce or effectively utilize construction byproducts; and techniques to effectively utilize waste disposal sites at ports.
Research Topics
Research and development were conducted on the following subthemes for efficient facility renewal, effective use of construction byproduct soil, utilization of waste disposal sites at sea, etc.
Research on techniques to improve or renew existing facilities
Research on effective use and techniques of treating construction byproducts
Research on management and utilization of waste disposal sites at sea
Activities in FY 2021
Research on techniques to improve or renew existing facilities
Study on process leading to rupture of pier structure for high definition of performance regulation While the performance requirements of piers can be broken down into different categories such as usability, repairability, and safety, the current performance specifications only cover the locations and amounts of residual displacement and plasticized hinges, etc. and fail to provide rules on their practical usability and repairability.To address such shortcomings, it is crucial to understand the fracture process of entire pier structures in detail, including the behavior of their components following yielding and plasticization. For this purpose, we examined several performance design concepts that could be applied to piers in the future, and identified potential issues that might exist with their performance assessment methods. Specifically, we considered an optimal approach to defining the performance requirements of non-anti-seismic facilities in withstanding accidental limit states and the performance regulations that would be applied to anti-seismic facilities. In addition, we identified and organized the potential issues that might exist with each of the performance assessment methods.
Development of quality evaluation method for ground improvement using geophysical exploration
As no effective method currently exists to three-dimensionally observe the status of improved materials underground after chemical grout is injected into inhomogeneous ground to prevent liquefaction, we conducted a study to establish methods of evaluating the quality of improved ground and construction management based on geophysical surveys that would not require soil sampling.Furthermore, we conducted an laboratory model experiment to examine the applicability of our geophysical survey method that is capable of real-time monitoring to the investigation of the changes in ground condition that would occur following chemical grout injection.
Research on effective use and techniques of treating construction byproducts
Development of core-less soil investigation and fundamental study to establish Digital Soil Mechanics
To improve the existing ground survey methods that utilize digital data including CT images and also develop a novel ground survey method, we are developing an"in-situ digital sampling method" that involves X-ray CT scanning of the core of in-situ ground, along with a series of testing and analysis techniques for evaluating the engineering characteristics of the ground based on the acquired CT images.For this purpose, we used the results of the model experiment conducted in FY 2020 to improve our drilling machine that has a built-in X-ray CT scanner and conducted another drilling test, which revealed that the drilling was able to penetrate the ground to the specified depth and scan the core there. The images obtained were so clear that we could discern the gravel particles in the ground.
Effect of defective part of solidified body on its internal stability
We performed numerical analysis to examine how weak sections would affect the stress-strain relationship of unconfined compression test, varying the strength ratio of weak and sound sections, weak section size, and the locations of the weak sections within the specimens. The analysis indicated that, if the solidified specimens contained some weak sections, the strain at failure would not increase, while exhibiting the same effects as crack-type disturbances that would only result in decreased strength. In addition, we placed a clay slurry that had been frozen with liquefied nitrogen in a mold, poured a slurry of cement-improved soil into the mold, and cured it to create specimens having unimproved weak sections, and conducter uniaxial compression test. The uniaxial test, during which the content ratio and locations of the weak sections were changed in various ways, revealed that the specimen that had weak sections more widely distributed across its mass was less affected in terms of its uniaxial strength deterioration.
Research on management and utilization of waste disposal sites at sea
On this research topic, we continue to gather information on the needs related to the land use of the sites and identify the issues involved.
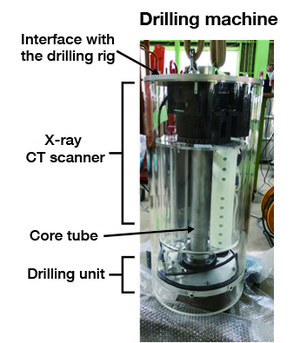

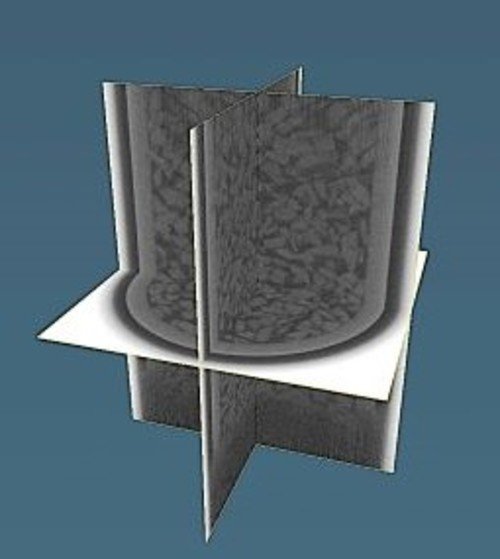
Drilling machine with built-in-X-ray CT scanner and drilling experiment/ CT image captured under ground after drilling
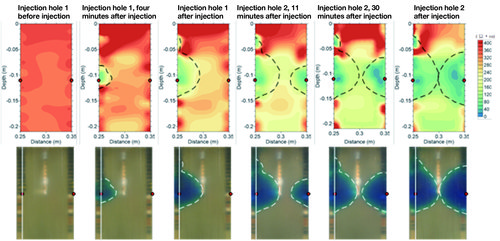
Real-time measurement results
(top: geotechnical survey; bottom: actual ground condition)

Comparison of weak-section ratios and peak strengths



