メッシュレス法による偏微分方程式モデルへのデータの同化
PDE-constrained optimization
観測データをモデル化する場合、
モデルが陽関数であれば、最小二乗法やグリッドサーチなどの手法を用いることで比較的容易にできますが、
モデルが偏微分方程式で与えられた場合には、さほど簡単ではありません。
偏微分方程式モデルはメッシュ数を増やすと基底関数の数が増え、短周期の関数がデータのノイズに敏感に反応して、
望まない解に導くことが多々発生します。
Modeling observed data is relatively easy when the model is an explicit function,
using methods such as least-squares and grid search,
but not so easy when the model is given as a partial differential equation (PDE).
Partial differential equation models increase the number of basis functions as the number of meshes is increased,
and the short-period functions are sensitive to noise in the data, often lead to undesired solutions.
この研究ではこうした望まないノイズの成長を抑制する手法として、
ラプラシアンフィルタを処罰関数として最適化評価関数に加えることを考えました。
In this study,
We considered adding a Laplacian filter as a penalty function
to the optimization evaluation function
as a method to suppress such unwanted noise growth.
潮流の分潮(M2)を対象として、メッシュレス法(MLS)と制限付き最小自乗法(CLS)を組合せたコードを作成し、
評価関数にラプラシアンフィルタを導入することの効果を検討しています。
Specifically,
a code combining the meshless method (MLS) and the restricted least-squares method (CLS) was created
for the tidal alteration (M2)
to study the effect of introducing a Laplacian filter in the evaluation function.
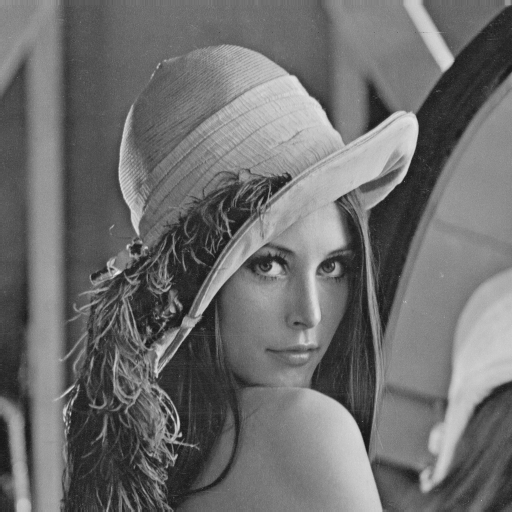

|
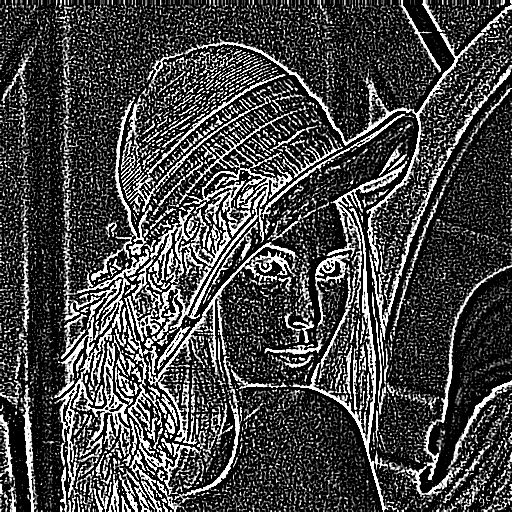

|
|
Example of Laplacian filter applied to "Lena"
(Laplacian filter extracts steep change of value)
|
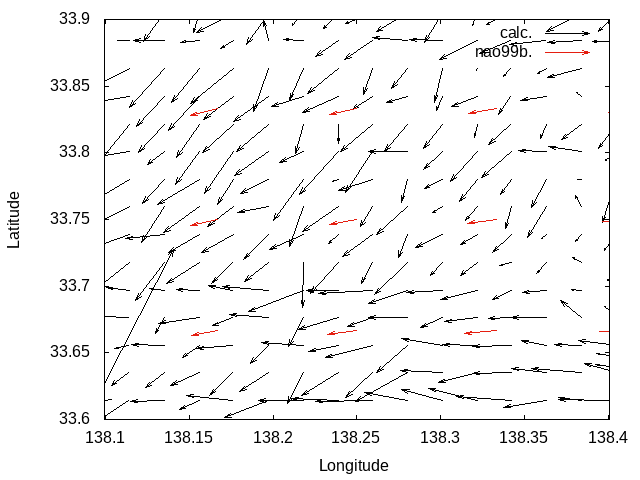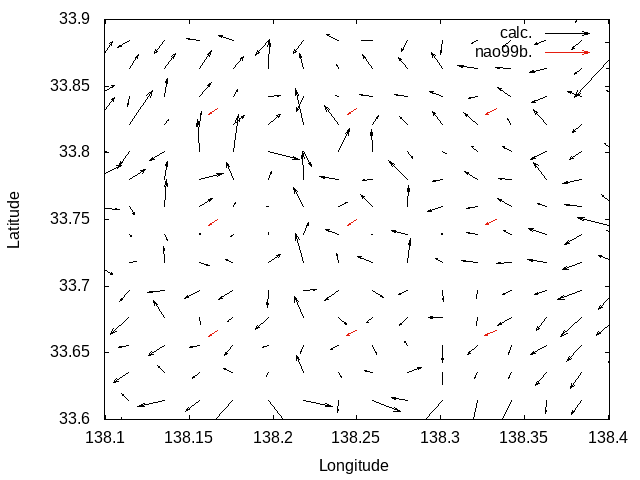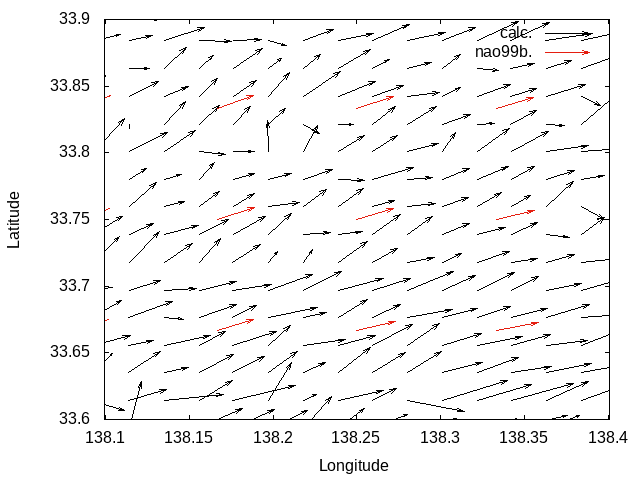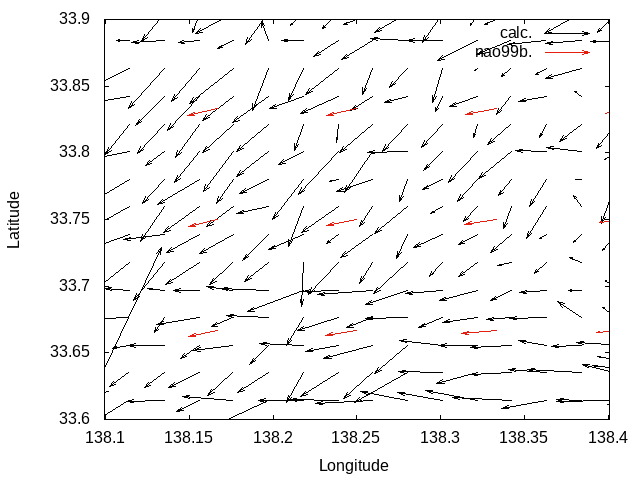
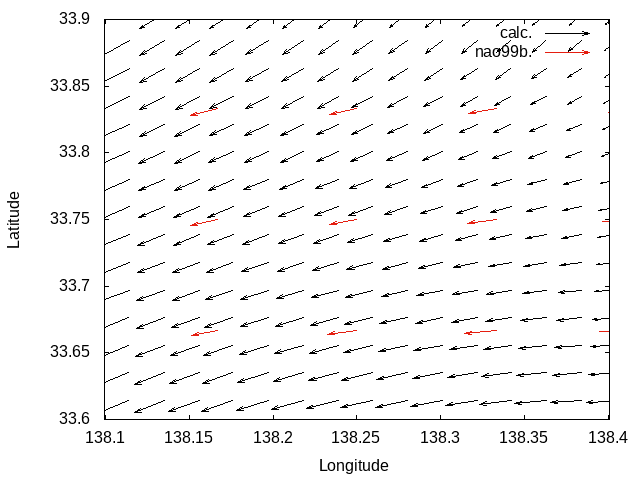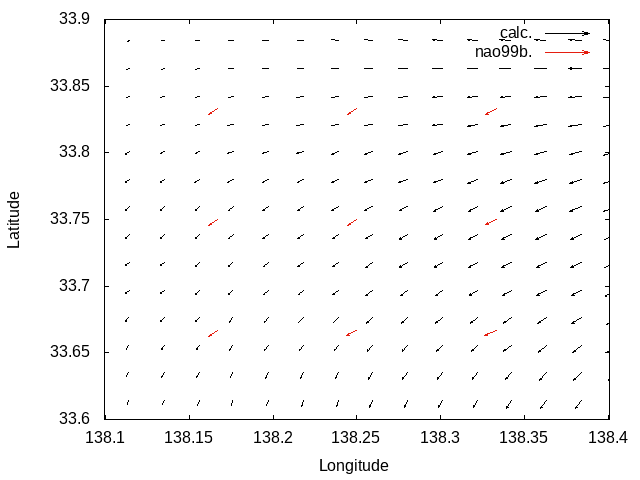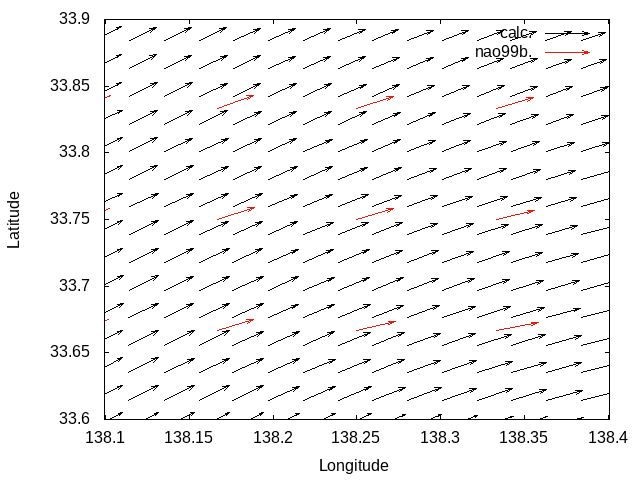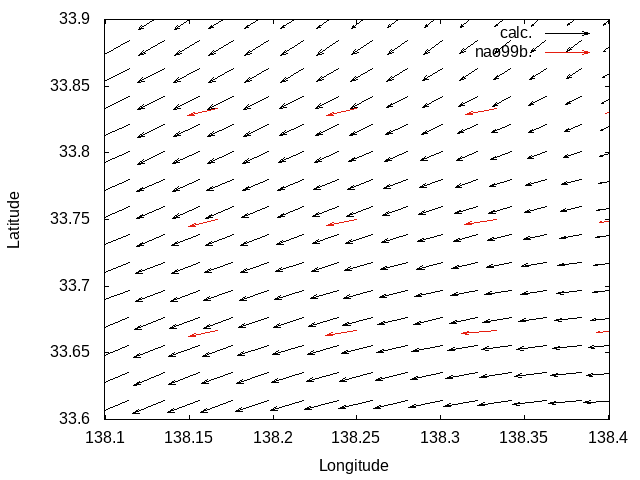
Without Laplacian filter
|
With Laplacian filter
|
|
M2 tidal current reproduction tests.
|
参考文献References








